Advancements in Yd2s Marker for Improved Crop Varieties
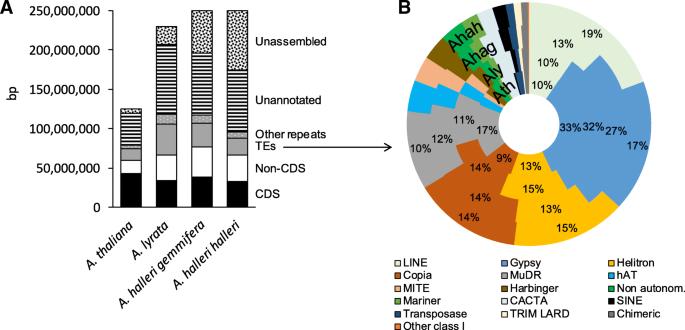
Yd2s is a molecular marker that plays a crucial role in agricultural and plant science. This marker is used to identify genetic variations in plants and has been found to be particularly useful in the development of new and improved varieties. Yd2s is a type of transposable element found in rice plants, responsible for the yellow pigment in the endosperm of the grain. By identifying variations in the Yd2s element, breeders can develop rice varieties with increased nutritional value while also developing varieties that are resistant to diseases, pests, and environmental stresses. Additionally, Yd2s can be used as a tool for studying the evolution and genetic diversity of rice and other related plant species.
Yd2s: A Transposable Element for Enhancing Rice Pigment Abundance and Distribution
Yd2s is a type of transposable element found in rice plants that can move from one location to another in a genome. The Yd2s element is responsible for the yellow pigment found in the endosperm of the grain. Researchers have found that the variations in the Yd2s element can affect the pigment’s abundance and distribution in the grain, making it a useful marker in developing new and improved rice varieties.
What is the significance of Yd2s as a marker in developing new and improved rice varieties?
Yd2s is a significant marker in developing new and improved rice varieties as it has been linked to yield and other important traits such as grain weight and length, which are traits of interest for improving rice production and quality.
Practical Applications of Yd2s in Plant Science and Agriculture
Yd2s has many practical applications in plant science and agriculture. Here are some examples:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| New rice varieties | Yd2s has been used to develop new rice varieties with increased nutritional value, such as higher levels of beta-carotene and iron. |
| Disease and pest resistance | Breeders have used Yd2s to develop rice varieties that are resistant to diseases and pests, such as bacterial blight and rice blast. |
| Study genetic diversity | Yd2s can be used as a tool for studying the evolution and genetic diversity of rice and other related plant species, providing insight into the history of plant domestication and human agriculture. |
Overall, Yd2s is a valuable tool for researchers and breeders looking to develop new and improved crop varieties. Its potential applications in nutrition, disease resistance, and evolutionary biology make it an exciting prospect for plant scientists and agricultural professionals.
What are the potential applications of Yd2s in plant science and agriculture?
Yd2s have potential applications in plant science and agriculture, such as improving crop yield and being used as a tool for genome editing.
Challenges of Yd2s in Rice Plants
One of the challenges with Yd2s is detecting and analyzing the element in rice plants.
The complex genetic interactions of Yd2s with other traits in rice can further complicate its use as a marker.
- Difficult to detect: The Yd2s element can be difficult to detect and analyze in rice plants due to its complex structure and location within the genome.
- Complex genetic interactions: Yd2s interacts with other genetic traits in rice, which can complicate the analysis and interpretation of data derived from the marker.
Despite these challenges, Yd2s remains an important tool for plant scientists and breeders looking to develop new and improved crop varieties.

What are the challenges of detecting and analyzing Yd2s in rice plants?
The challenges of detecting and analyzing Yd2s in rice plants include genetic complexity, variable expression levels, and the need for specialized techniques for detection and characterization.
Yd2s holds enormous potential for agricultural and plant science. Its ability to identify genetic variations in plants has already enabled breeders to develop new rice varieties with increased nutritional value and resistance to diseases and pests. The marker can also be used to study the evolution and genetic diversity of rice and related plant species. With a growing global population, the development of new and improved crop varieties is becoming increasingly important. Yd2s provides an invaluable tool to meet this challenge.
As researchers gain a better understanding of the Yd2s element and its interactions with other genes, it is likely that more applications for the marker will be discovered. However, there are still several challenges associated with Yd2s that need to be addressed. These include difficulties in detecting and analyzing the element in rice plants, as well as its complex genetic interactions with other traits in rice. Nevertheless, the potential benefits of Yd2s make it a key tool for researchers and breeders looking to advance agricultural practices and feed a growing global population.
In conclusion, Yd2s is an important molecular marker that offers many potential benefits for agricultural and plant science. Its ability to identify genetic variations in plants can help breeders develop new and improved crop varieties with increased nutritional value, resistance to diseases and pests, and environmental stresses. Despite the challenges associated with using Yd2s, its potential benefits make it a valuable tool for researchers and breeders looking to address the challenges of global food security.



